Explain Diversity In The Living World (Class 11 – Biology) – Notes.
Notes for NCERT Class 11 Chapter 2 Biological Classification: Biological classification is the process by which biologists group living organisms which, are classified on the basis of their similarity. Classification is essential for the convenient study of living organisms. It is required to identiRead more
Notes for NCERT Class 11 Chapter 2 Biological Classification: Biological classification is the process by which biologists group living organisms which, are classified on the basis of their similarity. Classification is essential for the convenient study of living organisms. It is required to identify different varieties of organisms. It helps in the correct identification of many organisms. It leads to the evolution of organisms. It also establishes phylogenetic relationships among organisms. Carolus Linneuas was one of the scientists to classify organisms.
NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 02 Biological Classification: The practice of classifying organisms based on shared characteristics is known as biological classification. Linnaeus proposed two areas of classification. He divided organisms into two kingdoms: the animal kingdom (Animalia) and the plant kingdom (Plantae). The classification of the two kingdoms had some disadvantages, such as the impossibility of distinguishing between eukaryotes and prokaryotes, unicellular and multicellular species, and photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic organisms. As a result, the field continued to grow and served as a primary example of R.H. Whittaker’s classification of the five domains or kingdoms.
Biological Classification
Two Kingdom Classification
Two kingdom classification was given by a biologist, Carolus Linnaeus. He classified organisms into two kingdoms, i.e. Plantae (included all plants) and Animalia (included all animals).
Disadvantages of Two Kingdom Classification
This system didn’t distinguish between the following types of organisms-
- Eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Unicellular and multicellular organisms
- Photosynthetic (green algae) and non-photosynthetic (fungi) organisms
Five Kingdom Classification
In 1969, R.H. Whittaker proposed the five-kingdom classification. He classified those five kingdoms as Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. He primarily used the following criteria for classification:
- Cell structure
- Body organisation
- Mode of nourishment
- Reproduction
- Phylogenetic linkages or relationships

Kingdom Monera
Bacteria are the main members of this kingdom. Kingdom Monera is further divided into:
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria or true bacteria

Archaebacteria
They are special bacteria as they can withstand extreme environmental conditions because of their different cell wall structure. They can be:
- Thermoacidophiles: They are found in the hot springs
- Halophiles: They are found in the salty areas
- Methanogens: They are found in the marshy areas/ gut of ruminant animals (production of biogas)
Eubacteria or True Bacteria
They have rigid cell walls and flagellum (locomotion), if motile. They can be photosynthetic autotrophs, chemosynthetic autotrophs and heterotrophs.
- Photosynthetic Autotrophs: Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae, have chlorophyll a), Nostoc and Anabaena are their common examples. They are surrounded by a gelatinous sheath or mucilaginous covering, which protects them from wetting. They fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts (significance)
- Chemosynthetic Autotrophs: These are the bacteria which oxidise inorganic substances, e.g. nitrates, nitrites and ammonia and use the released energy for ATP production. They recycle nutrients, e.g. nitrogen, phosphorous, iron and sulphur (significance).
- Heterotrophs: They are decomposers. Some of them are pathogens and some are beneficial as they are helpful in making curd from milk, producing antibiotics, and fixing atmospheric nitrogen in leguminous plants (significance).

Heterocyst
Reproduction in Bacteria
They reproduce by asexual mode- binary fission, sexual mode- transfer of DNA and spore formation in unfavourable conditions.

Mycoplasma
They are the smallest organisms which lack cell walls. They can survive in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic). They cause diseases (pathogens).
Kingdom Protista
They are single-celled eukaryotes. They include:
- Chrysophytes
- Dinoflagellates
- Euglenoids
- Slime moulds
- Protozoans
| Classification of Protista | Characteristic Features | Examples |
| Chrysophytes (chief producers in oceans) | Their cell walls form two overlapping shells, which are fit together and embedded with silica which, makes them indestructible. So, cell wall deposits and their accumulation leads to ‘diatomaceous earth’. This soil can be used to polish things, and filter oils and syrups. | Diatoms and golden algae (desmids) |
| Dinoflagellates | They show rapid multiplication and make the appearance of sea red (bioluminescence). Toxins released by them can kill other aquatic animals. | Red dinoflagellates (Example: Gonyaulax) |
| Euglenoids | They have a pellicle protein-rich layer) which keeps them flexible | Euglena |
| Slime Moulds | During suitable conditions, they form plasmodium and during unfavourable conditions, plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies (spores inside) |
Acrasia, Plasmodiophorina |
| Protozoans | They are heterotrophs and live as predators or parasites. They are classified into four types | Plasmodium |
Types of Protozoans and their Features/ Diseases Caused
| Protozoans | Features/Diseases Caused | Examples |
| Amoeboid Protozoans | They form pseudopodia to capture their prey. Some of them are parasites | Amoeba, Entamoeba |
| Flagellated Protozoans | Sleeping sickness, a disease caused by the parasitic forms | Trypanosoma |
| Ciliated Protozoans | Cilia (locomotion) and gullet, a cavity is present on the body | Paramoecium |
| Sporozoans | Some species cause malaria | Plasmodium |
Kingdom Fungi
Fungi are multicellular and the how heterotrophic mode of nutrition (saprophytes/parasites/symbiotic- mycorrhiza). Some fungi are unicellular, e.g. yeast.

Some Useful Fungi
Mushrooms and yeast are the most valuable fungi. Mushrooms are edible and are a good source of proteins. Yeast is used to make bread and cheese. Penicillium fungi are used to produce antibiotics.
Some Harmful Fungi
Some fungi cause diseases in both plants and animals, e.g. wheat rust disease is caused by Puccinia fungus.
Reproduction in Fungi
There are three modes of reproduction in fungi, i.e. vegetative, asexual and sexual.
- Vegetative Propagation: It takes place by fragmentation, fission and budding.
- Asexual Reproduction: It takes place by conidia or sporangiospores or zoospores.
- Sexual Reproduction: It takes place by oospores, ascospores and basidiospores.
Stages of Sexual Reproduction in Fungi
- Plasmogay- It is the fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes.
- Karyogamy- It is the fusion of two nuclei.
- Meiosis in zygote, gives rise to haploid spores.
In ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, the dikaryotic stage (n + n, i.e., two nuclei per cell) is formed, known as dikaryon and the phase is dikaryophase.
Four Major Groups of Fungi
| Classification of Fungi | Characteristic Features | Examples |
| Phycomycetes | They grow on decaying wood in moist sites and obligate parasites on plant bodies | Mucor, Rhizopus (bread mould fungi) and Albugo (parasitic fungi on mustard) |
| Ascomycetes (sac-fungi) | Neurospora is used in biochemical and genetic work. Some are edible, e.g. morels and truffles | Penicillium, yeast, Aspergillus, Claviceps and Neurospora |
| Basidiomycetes | Some are edible, e.g. mushrooms. Mushrooms are rich in protein | Agaricus (mushroom), Ustilago (smut) and Puccinia (rust fungus), Mushrooms, bracket fungi, puffballs |
| Deuteromycetes | They are known as ‘Imperfect Fungi’ because in this group, only asexual or vegetative phases are seen. Some fungi of this group are saprophytes or parasites while the majority are decomposers of litter, which aid in mineral cycling | Alternaria, Colletotrichum and Trichoderma |
Kingdom Plantae
All eukaryotic organisms that contain chlorophyll, usually known as plants, are classified as Plantae. A few species, like parasites and plants that feed on insects, are partially heterotrophic. Insectivorous plants include bladderwort and Venus fly traps, and parasites like Cuscuta feed on them. The eukaryotic structure of plant cells has large chloroplasts and a cell wall comprised primarily of cellulose. Algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms are all part of the plant kingdom.
Alternation of Generation
The haploid gametophytic and the diploid sporophytic phases of a plant’s life cycle alternate with one another. Various plant families have different haploid and diploid phase lengths and whether they are independent or reliant on others.

Kingdom Animalia
They are multicellular and heterotrophic (show the holozoic mode of nutrition) eukaryotes. They lack cell walls. Almost, all the animals show locomotion. Sexual reproduction occurs by the fusion of male and female gametes which give rise to an embryo followed by repeated cell divisions.
Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
The differences between viruses, viroids and prions are given below:
| Viruses | Viroids | Prions |
| They are oblique intracellular agents | They are oblique intracellular agents | They are the abnormal form of a cellular protein |
| They have either DNA or RNA which is surrounded by a protein coat | They consist of only RNA. The protein coat is absent | They don’t possess DNA or RNA. Only protein coat is present |
Bacteriophage
Bacteriophages are also known as phages. These are the viruses which infect and replicate in the bacterial cells.

Tobacco Mosaic Virus
The tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) consists of single-stranded RNA. It infects tobacco plants and members of the family Solanaceae. The infection can cause some patterns like a mosaic, which shows mottling and discolouration on the surface of the leaves.

Lichens
The close association of fungus and algae form lichens. They are found in a pollution-free environment. Lichens are used in deodorant, pH papers, insense-sticks, toothpaste and perfumes. The fungal component is known as mycobiont and the algal component is known as phycobiont.
FAQs on Biological Classification
Q1: What are the Commercial Applications for Heterotrophic Bacteria and Archaea?
Answer:
Heterotrophic Bacteria: They help with nitrogen fixation, ammonification and nitrification. In addition, Rhizobium bacteria, they maintain soil fertility. Other members produce dairy products such as cheese and cottage cheese. Archaebacteria: Methanogens in animal feces produce biogas.
Q2: Write Some Plant like and Animal-like Features of Euglena.
Answer:
Plant-like features are:
- Euglena has plastids which help in photosynthesis
- Some of the species of euglena have carotenoid pigments, which give it red colour
Animal-like features are:
- Euglena doesn’t have a cell wall
- Flagella are present for locomotion
Q3: What Function Do Fungi Play in Our Daily Lives?
Answer:
See lessMushroom and yeast are the most useful fungi. Mushrooms are edible and are a good source of proteins. Yeast is used to make bread and cheese. Penicillium fungi is used to produce antibiotics.

Diversity In The Living World Each residing life form will in general share highlights like development, upkeep of homeostasis, propagation, utilization of energy, adaption, and so forth. These highlights help to recognize various species and furthermore prove to be useful in laying out a connectionRead more
Diversity In The Living World
Each residing life form will in general share highlights like development, upkeep of homeostasis, propagation, utilization of energy, adaption, and so forth. These highlights help to recognize various species and furthermore prove to be useful in laying out a connection between organic entities with a typical hereditary part.
Biodiversity: Biodiversity is every one of the various types of life you’ll track down in one region — the range of creatures, plants, growths, and even microorganisms like microbes that make up our normal world. Every one of these animal categories and living beings cooperates in environments, similar to a multifaceted web, to keep up with equilibrium and back life. Biodiversity upholds everything in nature that we want to get by food, clean water, medication, and asylum.
Features of Living World
Diversity in the Living World
The world is overwhelmed by plenty of living organic entities living in the land, water, ice, sweets, and so forth. Each living organic entity is one of a kind of structure, body capabilities, hereditary make-up, etc. The living life forms found in various natural surroundings have different primary organs or capabilities created according to the states of their environment. Organic entities have advanced to adjust to their evolving surroundings. Various sorts and classes of life forms possessing various conditions are known as biodiversity. Districts that are warm and damp have more different organic entities and are called super biodiversity.
People have advanced from primates. However, presently they don’t appear to be comparative in any capacity. Likewise, every individual is not quite the same as the other. Each individual has an alternate skin tone, hair tone, and eyes, and generally significant of everything is hereditary cosmetics. And that implies that the qualities of each and every individual are unique.
In this manner, to recognize better, we have made gatherings of creatures that in some way seem to be comparative and have a few utilitarian and primary similitudes. This is known as order. There are different variables that impact the order of creatures. It is significantly done based on the accompanying models
Classification System
The grouping of life forms is finished by two techniques. One is characterizing them into plants and creatures and the other one which is a five-realm framework is a more nitty-gritty and coordinated characterization of living beings:
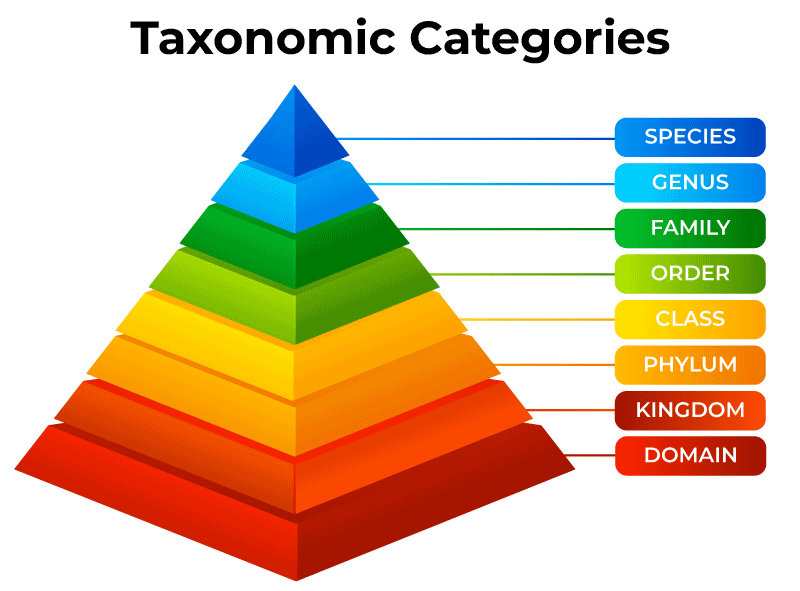
Hierarchy of Classification
Carolus Linnaeus additionally organized the organic entities into various scientific classifications at various levels. These scientific classifications in a chronic request are as per the following
Characteristics of Five Kingdoms
Kingdom Monera
These are unicellular prokaryotes. The life forms come up short on the evident nucleus. They might contain a cell wall. They might be heterotrophic or autotrophic in nature. For instance Bacteria, Cyanobacteria.
Kingdom Protista
Protista are unicellular and eukaryotic organic entities go under this group. They display an autotrophic or heterotrophic method of nutrition. They show the presence of pseudopodia, cilia, or flagella for headway. For instance one-celled critter, paramecium.
Kingdom Fungi
These are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms. They have a saprophytic method of nourishment which includes chemoheterotrophic extracellular processing. The cell wall in these organic entities is comprised of chitin. They live in a cooperative relationship with blue-green growth. For instance Yeast, Aspergillus
Kingdom Plantae
These are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms. The cell mass of these creatures is comprised of cellulose. They are heterotrophs and set up their own food through photosynthesis. Kingdom Plantae is partitioned into Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms. For instance Pines, plants, palm trees, mango trees, and so on.
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia is multicellular, eukaryotic living beings yet they don’t show the presence of cell walls. They are heterotrophs or creatures who can’t set up their own food. Both straightforward and complex life forms are found in this gathering and it’s an extremely general gathering of organisms. The organic entities are hereditarily diverse. They display an organ-framework level of organization. It is partitioned into various phyla like Porifera, Coelenterata, Echinodermata, Chordata, Annelids, and so on. For instance Earthworms, Hydra, and so on.
FAQs on Diversity In The Living World
Question 1: Why are living creatures arranged?
Answer:
Question 2: Why are the order frameworks changing occasionally?
Answer:
Question 3: What various measures could you decide to group individuals that you meet frequently?
Answer:
Question 4: What do we gain from distinguishing proof of people and the populace?
Answer:
Question 5: Given underneath is the logical name of Mango. Recognize the accurately composed name. Mangifera Indica
Answer: