What is Physics? Definition, History, Importance, Scope (Class 11)
The living world is a complex network of interconnected organisms that engage in metabolism, reproduction, and response to environmental cues. We are aware of how intricately connected everything in the living world is. The diversity of living forms on earth gives it a wonderful environment to liveRead more
The living world is a complex network of interconnected organisms that engage in metabolism, reproduction, and response to environmental cues. We are aware of how intricately connected everything in the living world is. The diversity of living forms on earth gives it a wonderful environment to live and thrive. The abundance of diversity suggests the presence of numerous species with unique characteristics. The fact that an organism is either a living thing or a non-living entity is its most striking characteristic. As a result, in order to distinguish between a living item and a non-living one, we first need to define what a “living being” actually is.
What is ‘Living’?
Any organism that breathes and moves is considered ‘Living’. Any life form that exhibits or possesses the qualities of life or being alive is referred to as a living thing. The basic traits include having an organized structure, requiring energy, reacting to stimuli and changing their surroundings, and having the ability to reproduce, grow, move, metabolize, and die. The three Domains that make up the current classification of living things are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya.
Characteristics of Living World
All living organisms grow and increase in mass and number of individuals. Growth, reproduction, ability to sense the environment and mount a suitable response is unique features of living organisms. Given below are some characteristic features of the Living world:
Respiration
- Aerobic respiration: Aerobic respiration is a chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from sugars. Aerobic respiration is also known as aerobic metabolism and cell respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. examples include alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Nutrition
- Autotrophic Nutrition: It is a type of nutrition in which plants make their own food .they are interdependent on themselves. example- plants. Autotrophic nutrition is of two types: phototrophic, and chemotrophic.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: It is a type of nutrition in which an organism is dependent on another organism for food. example -humans. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous.
Excretion
The process of moving out waste material from the body is known as excretion.
Locomotion/Movement
Locomotion is a term used to describe a movement of an organism from one place to another.
Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction: A process where a single gamete is responsible for reproduction to take place i.e., new offspring is produced from a single parent. Examples: hydra and paramecium.
- Sexual Reproduction: Process where both the gametes take part in reproduction. Examples: fishes, and mammals.
Structural Organisation
- Unicellular: It is also known as a single-celled organism and only single cells perform all the functions needed for an organism to live. example- protozoa and Protista.
- Multicellular: Multicellular organisms consist of many cells to perform different functions. example-Dogs, cows.
Diversity
A large variety of anything is known as diversity. Diversity is a vast term to include different species, genes, and ecosystem levels. Thomas Lovejoy introduced the term biological diversity in 1980.
Biodiversity
A large variety of organisms or terms used to refer to the number of varieties of plants and animals on earth is termed biodiversity. there are three types of biodiversity: genetic, species, and ecological diversity. There are over 15 Lakh species in the world of which 10 Lakh are animals(8 Lakh of insects and 2 Lakh of others) and 5 Lakh of plants.
Nomenclature
The scientific naming of organisms is known as nomenclature. Nomenclature is defined as the language of sculpture. The scientific name of mango is written as Mangifera indica.
Rules of Nomenclature
- Latinised names are used.
- The first word represents the genus and the second word is the species name.
- Printed in italics, if handwritten then underline separately.
- The first word starts with a capital letter while the species name is written in small letters.
ICBN International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (This is for giving scientific names to plants).
ICZN International Code of Zoological Nomenclature(This is for giving scientific names to animals).
Classification
Grouping organisms into categories on the basis of similarities and differences is known as classification. classification is the process by which anything is grouped into systematic categories based on some easily observable characteristics. For example, we easily recognize groups such as plants or animals, dogs or cats, insects, or reptiles.
Need of Classification
Classification is done to organize the vast number of plants and animals into categories that could be named, remembered, studied, and understood. classification avoids confusion among the different varieties of organisms. Moreover, it makes the study of organisms easier.
Given below are some scientist’s contributions to biology
- Carolus Linnaeus (Father of Taxonomy): He gives the 2 kingdoms system.
- Hackel: He gave the 3 kingdom systems.
- Copeland: He gave the 4 kingdom systems.
- R.H Whittaker: He gave the 5 kingdom system which is the popular one.
- Carl Woese: He gave the 6 kingdom system and is the latest.
Taxonomy
The study of principles and procedures of classification is termed taxonomy. Based on characteristics, all living organisms can be classified into different taxa. This process of classification is taxonomy.
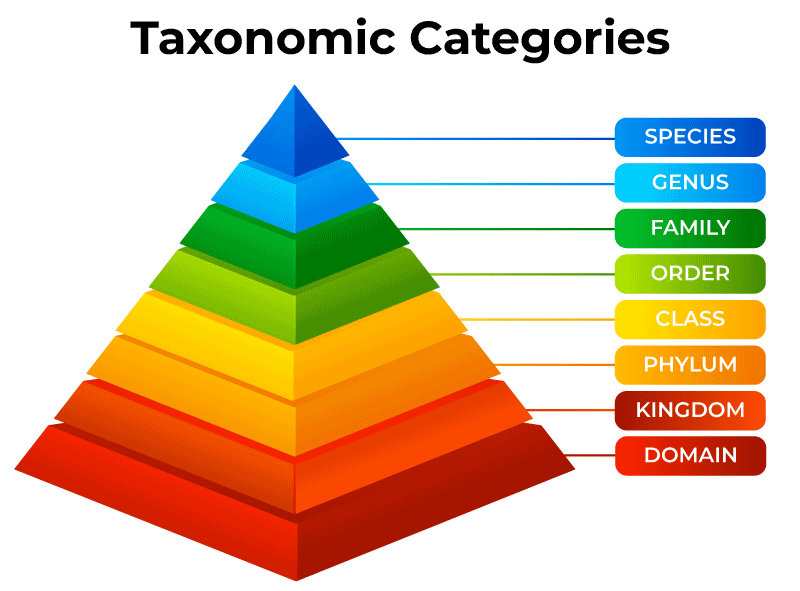
Taxonomic Categories
A. P. Candolle is credited with coining the term “taxonomy,” which refers to the seven main taxonomic categories. It is the listing of categories from the top-most kingdom to the bottom-most species, either in ascending or declining orders. There are two kinds in the hierarchy: intermediate and mandatory. From kingdoms to species, Obligate is rigidly adhered to, yet Intermediate is the exact reverse.
- Species: The smallest and most fundamental distinction in classification is the species. It describes a population that is comparable in terms of form, shape, and reproductive characteristics. Similar reproductive characteristics can lead to the formation of fertile siblings.
- Genus: This is the grouping of a number of closely related species that share linked features and are thought to have shared ancestors. For instance, the genus Panthera is where the leopard and cat belong.
- Family: Families are associations of connected genera. The vegetative and reproductive characteristics are used to categorize the families. The Felidae family includes animals like tigers and lions as examples.
- Order: It is the combination of one or more common families, which is regarded as a higher category. Felidae family members participate in the Carnivora order.
- Class: A class designates a division in a phylum made up of one or more orders. All mammals, including gorillas, monkeys, humans, and gibbons, are included in the Mammalia class.
- Phylum: It contains a group of related classes. Mammalia, along with reptiles, fish, amphibians, and birds, make up the phylum Chordata.
- Kingdom: The highest taxonomic classification known as a kingdom is given to every animal that belongs to various phyla. The kingdom Animalia and Plantae encompasses all living things, including both plants and animals. A taxon is a classification that identifies an organismal group based on external characteristics.
FAQs on Living World
Q1: Define the following terms: Phylum, and Class.
Answer:
- Phylum– Classes comprising animals like fishes, amphibians, reptiles, and birds along with mammals constitute the higher category called phylum. All these, based on the common features like the presence of notochord and dorsal hollow neural system, are included in phylum Chordata.
- Class– This category includes related orders. For example- the order primate comprising monkey, gorilla, and gibbon is placed in class Mammalia along with the order Carnivora which includes animals like tiger, cat, and dog.
Q2: How is a key helpful in the identification and classification of organisms?
Answer:
The key is defined as the taxonomical aid used to identify and classify plants and animals based on their similarities and differences. Keys are generally analytical in nature.
Q3: Define a taxon.
Answer:
Taxon is plural of taxa, it is the taxonomic unit of any rank. ARISTOTLE is known as the father of taxonomy.
Q4: Why are living organisms classified?
Answer:
See lessLiving organism are classified due to the following reasons:
- To make study of organism easy.
- To avoid confusion.
- To learn the interrelationship among the various organisms.










 Formula for Gravitational Force,
Formula for Gravitational Force,

 Strong Nuclear Force
Strong Nuclear Force
The most curious mind out of all the species is the mind of homosapiens. Humans are always curious about the nature around them and the magic laws on which it functions. The sun always rises in the east and sets in the west, the moon appears at night and the sun appears in the day, and so on. All thRead more
The most curious mind out of all the species is the mind of homosapiens. Humans are always curious about the nature around them and the magic laws on which it functions. The sun always rises in the east and sets in the west, the moon appears at night and the sun appears in the day, and so on. All these questions not on make humans curious but make them think and discover about the different theories of nature and by doing so, humans soon started discovering physics in order to discover the world and its mystery. Let’s learn what is physics in more detail,
What is Physics?
The word “science” has been originated from a word in the Latin dictionary named “Scientia” which means “to know”. Therefore, in one way, it can be said that science is nothing but to know the working of everything, from nature to machines. Under science, a category well known is nature science, which is the study of the physical world around humans. Physics, chemistry, biology, geology, all these fields lie under nature science.
A basic discipline of nature sciences is physics. Physics is also a word taken from the Latin dictionary which means nature. In Sanskrit, it is known as “Bhautiki” which is the physical world around. The definition of physics is not accurately present but it can be said that physics is the study of all basic laws of nature and their manifestation in a different phenomenon.
Physics as a whole explains the diverse physical phenomenon with respect to concepts and laws. For instance, from the falling off an apple on the ground and the law associated with it to the revolving of planets around the sun, to electromagnetism and its effects, physics defines it all. The major concept involved in physics is the use of basic approaches for bigger and complex problems, the process of solving a complex problem by breaking them into smaller parts is called reductionism. Then the act of unifying different laws is called unification.
History of Physics
The word science has been originated from a Latin word named “Scientia” which means “to know”. The word “Physics” has been originated from a Greek word named “Phusike” which means nature. In Sanskrit, physics is called “Vigyaan” which means “knowledge”, all of these words simply tell that physics is as old as the human species. Early civilizations like Egypt, India, Greece, etc, made a significant contribution in the field of physics. From the 16th century, Europe participated heavily and contributed. By the mid-twentieth century, science became an international enterprise and the rapid growth in the very field is on. The two major approaches in physics are already described above, they are unification and reductionism.
Importance and application of physics
Scope and Excitement of Physics
The scope of physics can be majorly understood by looking at its sub-divisions. There are basically two types of studies in physics, macroscopic physics, and microscopic physics. Macroscopic physics deals with phenomena on a terrestrial, astronomical scale, while microscopic physics deals with the phenomenon on an atomic, molecular, or nuclear scale. The macroscopic study is done mostly in classical physics that includes subjects like mechanics, thermodynamics, etc. The microscopic study is the study of the structure of the atom, etc. Classical physics is unable to contribute in this field and currently, quantum theory is referred for the microscopic level studies.
Therefore, it can be said that the scope of physics is really very vast. The study covers a plethora of physical quantities like length, mass, time, energy, etc. From the study of smallest quantities (ranging up to 10-30 or less) to the study of the quantities on an astronomical level (ranging up to 1020 or more).
Fundamental forces in Nature
Force is seen and experienced on a daily basis and is available on both macroscopic and microscopic levels. At a macroscopic level, apart from gravitational force, several kinds of forces are experienced, for instance, muscular force, contact forces, the elongation or compression of elastics, etc. On a microscopic level, there are electric and magnetic forces, nuclear forces, etc. Although, it was further observed that most of the forces defined or explained are derived from four fundamental forces. The four fundamental forces in nature are,
Conceptual Questions
Question 1: Which of the four fundamental forces is the weakest and the strongest?
Answer:
Question 2: What are the laws of conservation in nature?
Answer:
Question 3: On what two things the scope of physics is defined?
Answer:
Question 4: What part of the study is not handled by the classical study of physics?
Answer:
Question 5: Give an example of a weak nuclear force.
Answer:
See less